80+ Standard Continues to Drive Innovation

Happy Earth Day!
As the leader in high-voltage integrated circuits (ICs) for energy efficient power conversion, Power Integrations celebrates the spirit of Earth Day everyday with innovative technologies that save energy, lower CO2 emission and reduce the number of electronic components used.
The company actively supports the development of energy efficiency standards around the world. This Earth Day, we take a look at how one such standard continues to drive innovation and technical advancement in energy saving.
The announcement by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) of the 80+ efficiency standard for PC power supply units (PSUs) in 2004 was a transformational event. At the time, computer PSUs typically averaged between 65% and 75% efficient with power factors of 0.6 or less, and getting to 80% efficiency was a big deal. The technology existed to design more efficient PSUs, but there was no demand from computer or network equipment makers.
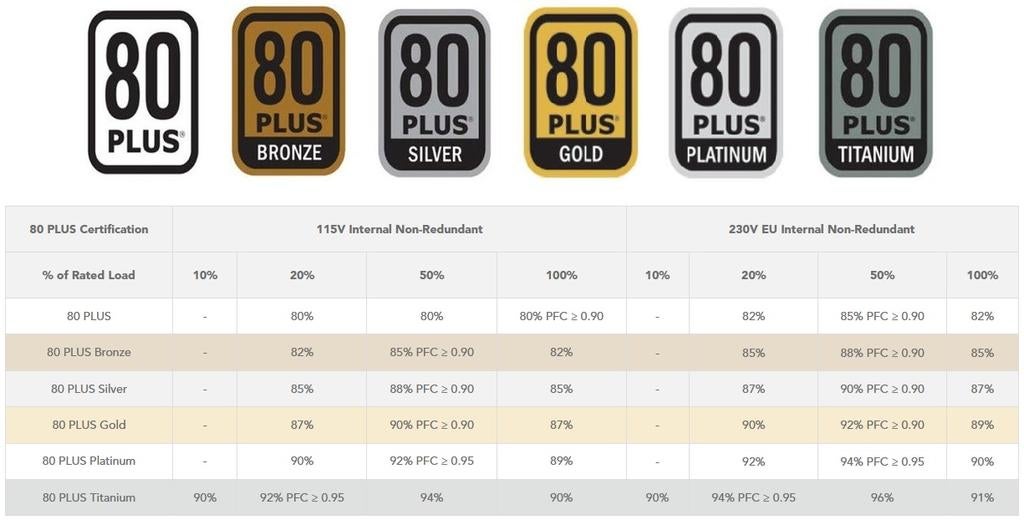
Immediately upon the launch of 80+, PSU designs began to change, using more active technologies and control techniques including active power factor correction (PFC), active clamps on the main converter stage and synchronous rectification on the output. Today, all five levels of 80+ (Bronze, Silver, Gold, Platinum and Titanium) require minimum efficiencies over 80%.
The changes are more dramatic than it might seem at first. With 80% efficiency, losses are 20%. At the Titanium level, efficiency of 92% is required, and losses are only 8%. That equates to a 60% reduction in losses.
The most important result of 80+ has been a continual innovation drive to enable the design of higher-efficiency PSUs for the same, or even lower, cost compared with previous generations of lower efficiency units. Silicon MOSFETs are very effective devices for getting up to initial Titanium efficiency levels. But innovation is driving designers toward non-silicon options.
Today, advanced PSUs are designed using gallium-nitride (GaN) power switches with component count reductions of 40% or more. Fewer components help to increase reliability and shrink solution size and cost. Users that invest in an 80+ PSU also get increased reliability, lower maintenance costs and lower total cost of ownership.
The Titanium level requires maximum efficiency of 96% for 230 VAC input and 94% for 115 VAC input, both at 50% load. The use of GaN can produce PSUs that deliver 98.3% efficiency over the entire load range and power factors of 0.96, exceeding the Titanium performance specifications.
80+ also educate users of computer equipment about the multiple benefits from using high efficiency PSUs. In addition to a lower electric bill, higher efficiency means less heat generated and less need for cooling, resulting in noise reduction from slower spinning fans, or even designs with no fan.
Conclusion
After 20 years, 80+ will continue to be relevant and drive innovation. The EU ErP (Ecodesign in Europe) Regulations are aligned with the 80+ certification on both single- and multi-output PSUs for data storage products and servers. Single-output PSUs are required to meet 80+ Platinum efficiency. In January 2023, that requirement will move up to Titanium efficiency. What’s beyond Titanium? We’ll soon find out, as in January 2026 the EU ErP Regulations are expected to increase efficiency requirements again, higher than Titanium.





